
: ~ $ git git commit -m "Add GitHub submodule" GitHub submodule push : ~ $ git clone : ~ $ git log -oneline : ~ $ git cd surface : ~ $ git submodule add : ~ $ git status : ~ $ git git add. The following is the list of commands performed in the GitHub submodule add example. Push the GitHub submodule add commit back to the server.

gitmodules file to the index and perform a git commit. gitmodules file is created in the parent project.
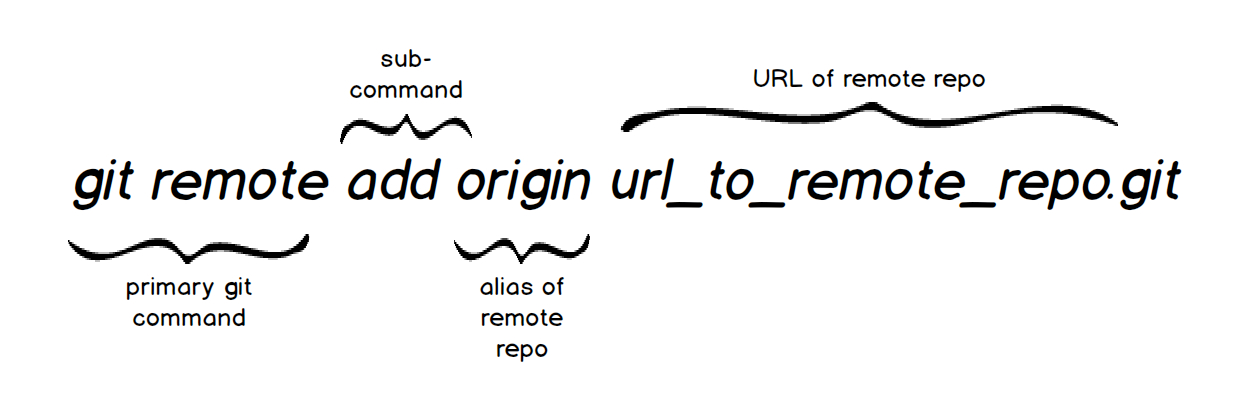
Issue a “git status” command to verify a. In the root of the parent, issue a “ git submodule add” command and provide the GitHub repository’s URL. Clone the parent or top-level repository. The following list of steps will add Git submodule GitHub relationships between two repositories: I will allow you to deduce on your own which one is the parent module and which one is the Git submodule. Run git rm -cached path_to_submodule (no trailing slash). If only `git rm the_submodule` (without prior `git submodule deinit the_submodule` is run, however, the submodules' entry in your. The files will be gone as well as the submodules' entry in the `.gitmodules` file (). `git rm the_submodule` will remove the submodule from the work tree. `git submodule init` and `git submodule update` will restore the submodule, again without commitable changes in your parent repository. Also, this will not be shown as change in your parent repository. This excludes the_submodule from `git submodule update`, `git submodule sync` and `git submodule foreach` calls and deletes its local content (). `git submodule deinit the_submodule` deletes `the_submodule`s' entry from. $ git submodule deinit the_submodule $ git rm the_submodule # renamed: old/path/to/submodule -> new/path/to/submodule `git status` output looks like this afterwards: Edit the file `**new/path/to/module**/.git`, make sure that the path in it points to the correct new location inside the main project `.git` folder, so in this example `gitdir. Typically there should be two more `.` then directories in the direct path in that place. Move the directory `.git/modules/**old/path/to/module**` with all its content to `.git/modules/**new/path/to/module**`.Įdit the `.git/modules/**new/path/to**/config` file, make sure that worktree item points to the new locations, so in this example it should be `worktree =. 
Remove the old directory with `git rm -cached **old/path/to/module**`. Make sure Git tracks this directory (`git add **new/path**/to`). Move all content from the old to the new directory (`mv -vi **old/path/to/module** **new/path/to/submodule**`). If needed, create the parent directory of the new location of the submodule (`mkdir -p **new/path/to**`). $ git mv **old/path/to/module** **new/path/to/module**Įdit `.gitmodules` and change the path of the submodule appropriately, and put it in the index with `git add. Tidying up your local and remote repository.Reflog - Restoring commits not shown in git log.Display commit history graphically with Gitk.mailmap file: Associating contributor and email aliases Cloning a Git repository having submodules.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
